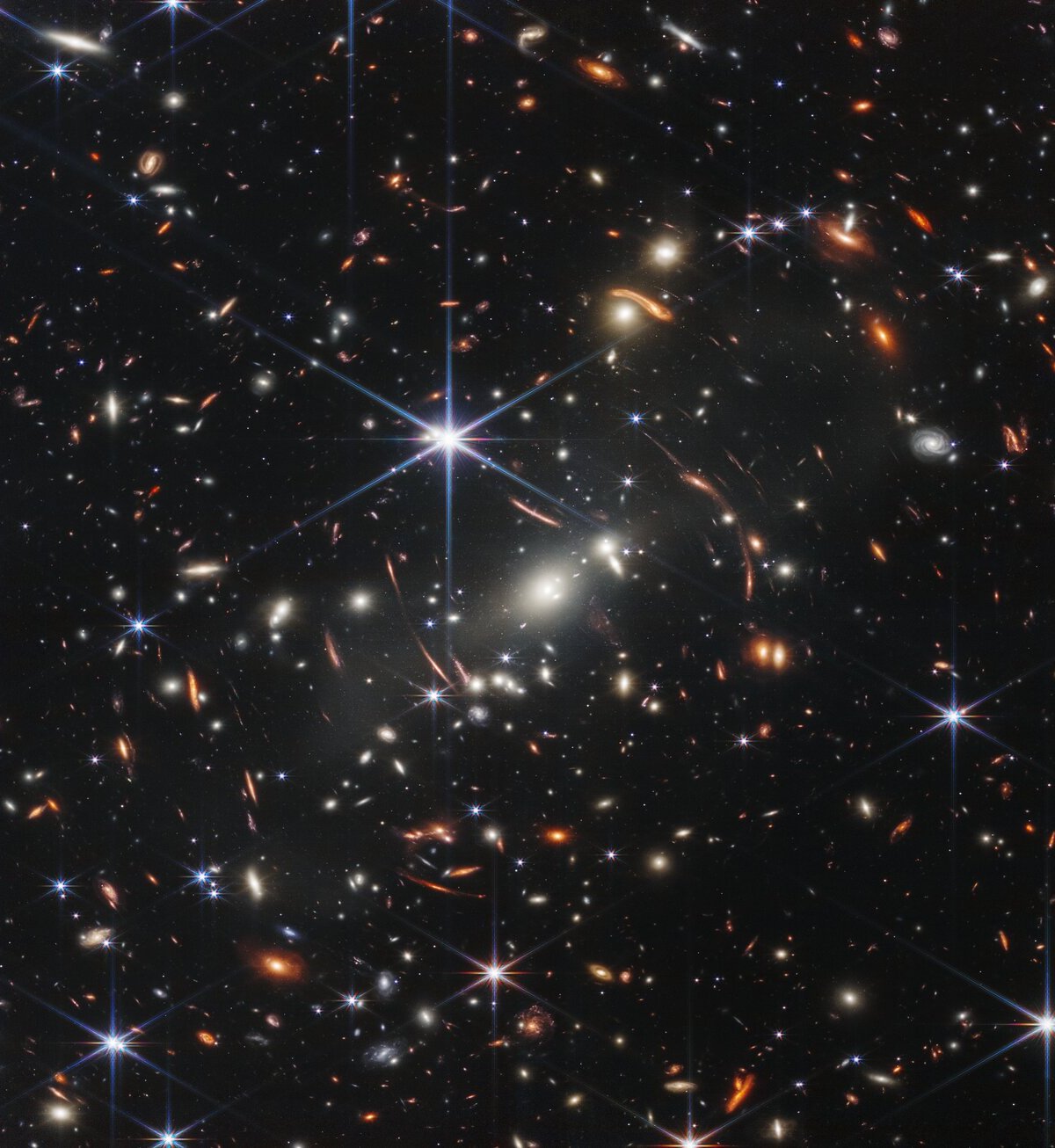
Although the word “universe” means “all together,” it is impossible to try to know all the matter and energy that this space-time continuum contains. As observation methods improve, We are discovering unthinkable truths on increasingly larger scales.
The universe itself is already huge, but it also hosts enormous objects that will amaze the scientific community and arouse the curiosity of astronomy enthusiasts. Here we show you some of the record holders from this dispute that you can’t see up close. Check out!
8 giants of the universe (so far)
Exoplanet GQ Lupi b
Discovered in April 2005 about 495 light-years from our Solar System and orbiting a young star of the same name, GQ Lupi was not immediately identified as an exoplanet due to its large orbit (twice as large as Pluto’s). ). It has even been confused with a brown dwarf star due to its size, which is 3.5 times the size of Jupiter.
Star UY Scuti

Its radius is approximately 1,700 times greater than that of the Sun. UY Scuti has been considered the largest known star since 2010. Although it surpasses our star in almost every respect, it is cooler, with a surface temperature estimated at 3,092°C (compared to the Sun’s 5,232°C).
Although it is relatively young (8-10 million years old), it is in the red supergiant stage. It heralds an explosive end “soon” when it will explode into a supernova and then into a black hole..
Tarantula Nebula

Tarantula, also known as 30 Doradus or NGC 2070, is the largest nebula and most active star-forming region in the Local Group, the cluster of galaxies that today includes the Milky Way. Its longest point is 1,800 light years It serves as a laboratory to study the formation and birth of stars.
Galaxy IC 1101

With an estimated diameter of 6 million light-yearsIC 1101 is the largest known galaxy in terms of width. This mega galaxy, which is almost 60 times larger than the Milky Way and approximately 2 thousand times larger, contains close to 100 trillion stars, making it the record holder for stellar population.
Read more:
TON 618 black hole

Located an impressive 18.2 billion light-years away from Earth, TON 618 has a mass between 60 and 100 billion times that of our Sun. Despite this distance, it appears quite bright because it is a quasar, a galactic nucleus fueled by material falling towards it. hole.
Only the diameter of the event horizon is more than 1 thousand AU (Unit that measures the distance between the Earth and the Sun).
Single object protocol stack SPT2349-56
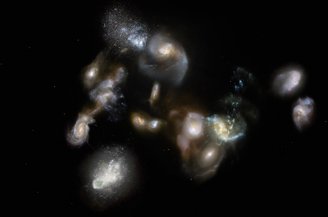
A protocluster, a galaxy cluster in the early stages of formation, gathers under the gravitational force of young and massive galaxies until they become a single object: In the case of SPT2349-56 it corresponds to 10 billion times the mass of the Sun, In fact, it’s squeezed into an area just three times larger than the Milky Way.
The biggest thing in the universe: The Great Wall of China Hercules-Corona Borealis

If a large galactic object fascinates you, imagine a series of galaxies with a wide variety of stars and star systems stretching more than 10 billion light-years. This is the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall, the largest known structure in the observable universe, discovered in November 2013 by mapping the distribution of gamma-ray bursts.
Supervoid in Eridanus

If there are records of huge structures There is also a huge region of space filled with voids. It is known to astronomers as the Eridanus SuperVoid, as it is a type of “hole”. This spot, which is 1.8 billion light-years in diameter, contains very little matter; strangely devoid of stars, gas, dust, or even dark matter.
Did you like the content? Tell us on our social networks and get the opportunity to share the article with your friends who love astronomy!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.













