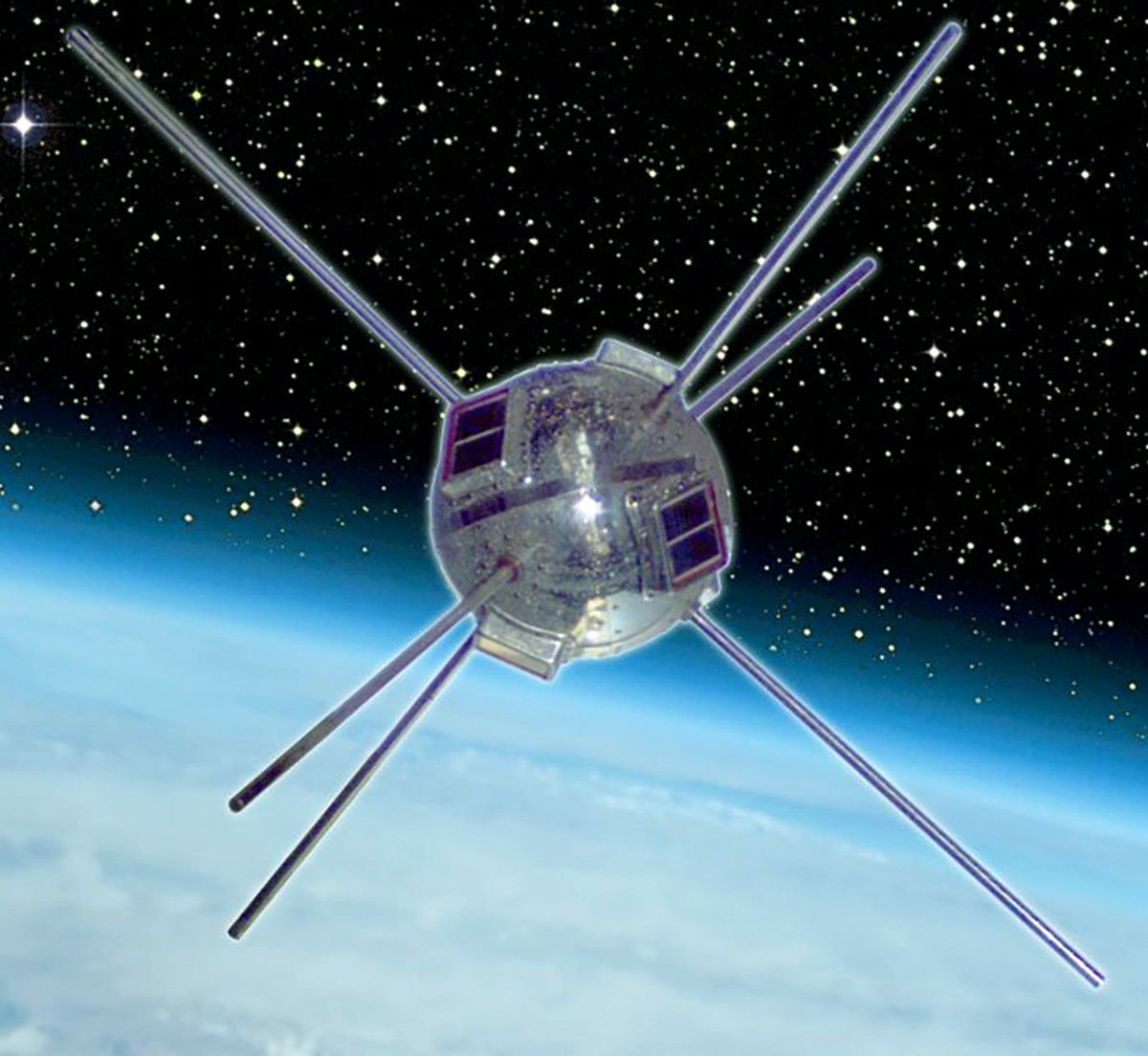
One of the first spatial devices of the cold war between the US and the Soviet Union, SO -CON, Vanguard 1 satellite continues to turn the world. It was used to examine the intensity of the high atmosphere that was released on March 17, 1958, measure the shape of the planet and ended the transmission in 1964.
Recently, a team of researchers and engineers in the US consultant company Allen Hamilton presented a 16.5 cm small diameter and a 1.47 kg weight to “retire”. The aim of this spatial archeology is to examine how the US Naval Research Laboratory equipment has been going on for years.
Vanguard 1 is one of the most valuable objects that have existed since the beginning of the space period ”, the province of Virginia published in January this year Aviation Research Center“Discover the options for useful tasks and loads using technology that can securely control and recover the satellite for work and imaging.”
History of Vanguard Satellite 1
When the Soviet Union placed it in the first satellite orbit, on October 4, 1957, Sputnik 1 caused a “God” in the US research laboratories. Worse, a pioneer prototype called TV3 (Test Tool 3), which was hurriedly released two months later, rose only 1.2 meters and exploded in a fire ball and became an international joke.
For this reason, the US Army accelerated sending to terrestrial Orbit Explorer 1 on 31 January 1958, and then Vanguard 1 was released by the navy about a month and a half later. The first satellite worked for only four months and in March 1970, the World Atmosphere was re -entry, but the second was in an elliptical orbit with Perigeum (close to Earth) at 660 km today and begged at 3,900 km.
In the last 67 years, this elliptical orbit, which allowed the orbit object to survive. Even in silence, the equipment is still monitored with terrestrial radars. Vanguard 1, which is a pioneer in the use of solar cells in space, reaches a speed of 27,000 km/h when perish and 16,200 km/h in the brightest period. This means that the orbit time is 2 hours and 14 minutes and only 42 minutes longer than the International Space Station (ISS).
How do scientists plan to save Vanguard 1?
Westar 6 and Plapa B2 communication satellites inspired by the 1984 NASA operation, and the space bus loading of them in the division of the booste allen scientists and engineers, using the ISS as a support point, proposing to place Vanguard 1 in a lower orbit.
However, the team says: Before capturing, a spaceship is sent to examine it closely. According to authors, it can be done in partnerships with space enthusiasts such as SpaceX to activate the task.
According to the article, the techniques shown in the possible healing of Vanguard 1 can form a foundation for “future tasks (removal of spatial ruins, capturing materials for orbit production, and even the discovery of the deep space.
What do you think about an older satellite recovery operation in the world? Beyond the symbolic movement, does the task add any value to science? Explain the story on your social networks and comment on these issues.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.